 US fl oz
US fl oz UK fl oz
UK fl ozRecent Conversions
Conversion Formulas: US vs UK Fluid Ounces
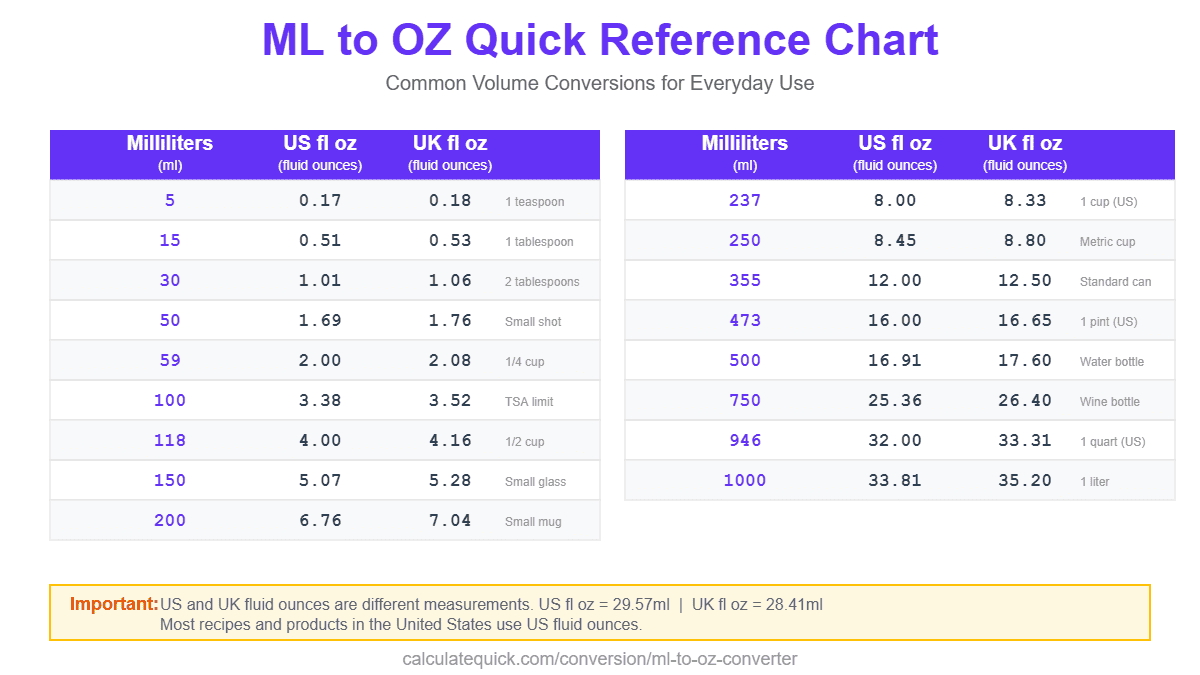
Converting milliliters to fluid ounces requires understanding which fluid ounce measurement system applies. The US fluid ounce equals 29.5735 milliliters, while the UK imperial fluid ounce equals 28.4131 milliliters. In percentage terms, this is a 4% difference affects recipe accuracy, product labeling, and precise measurements.
Milliliters to Fluid Ounces Conversion Table
| Milliliters (ml) | US Fluid Ounces | UK Fluid Ounces |
|---|---|---|
| 15 | 0.51 US fl oz | 0.53 UK fl oz |
| 30 | 1.01 US fl oz | 1.06 UK fl oz |
| 50 | 1.69 US fl oz | 1.76 UK fl oz |
| 100 | 3.38 US fl oz | 3.52 UK fl oz |
| 150 | 5.07 US fl oz | 5.28 UK fl oz |
| 200 | 6.76 US fl oz | 7.04 UK fl oz |
| 250 | 8.45 US fl oz | 8.80 UK fl oz |
| 500 | 16.91 US fl oz | 17.60 UK fl oz |
| 750 | 25.36 US fl oz | 26.40 UK fl oz |
| 1000 | 33.81 US fl oz | 35.20 UK fl oz |
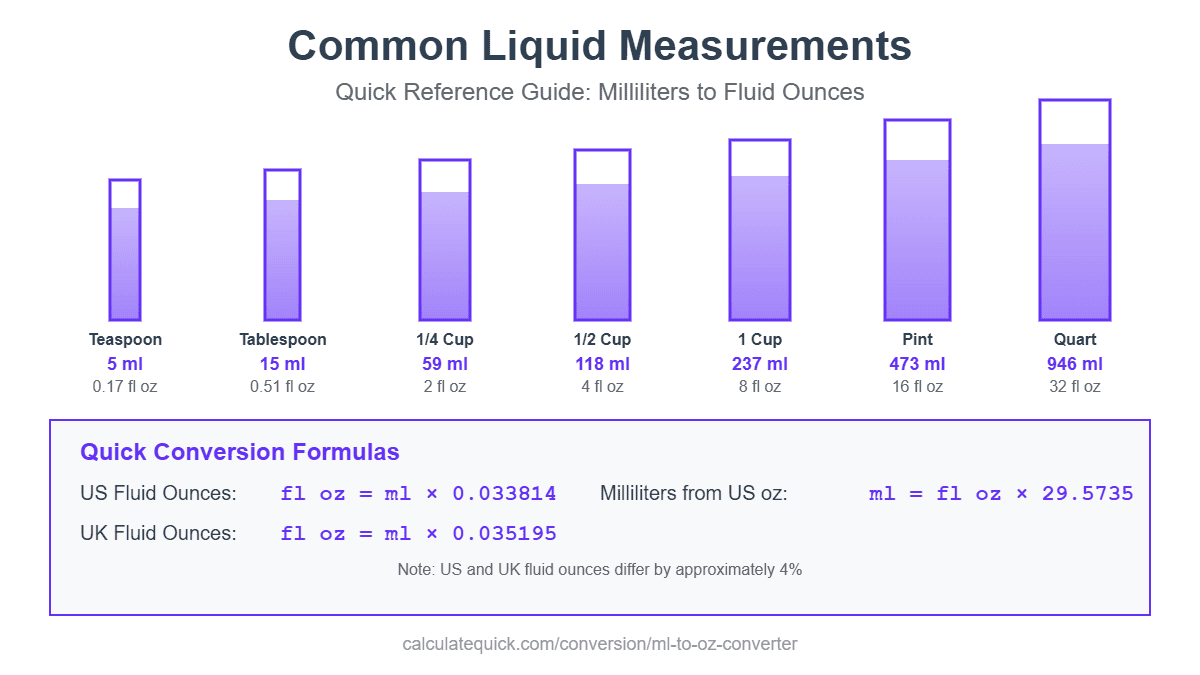
Cooking and Baking Measurements
American recipes use fluid ounces and cups while international recipes use milliliters and liters. A standard US measuring cup holds 236.59 milliliters (8 US fluid ounces). UK recipes traditionally use imperial measurements where one cup equals 284 milliliters (10 UK fluid ounces).
Common Cooking Measurements
| Measurement | Milliliters | US Fluid Ounces |
|---|---|---|
| 1 teaspoon | 5 ml | 0.17 fl oz |
| 1 tablespoon | 15 ml | 0.51 fl oz |
| 1/4 cup | 59 ml | 2 fl oz |
| 1/2 cup | 118 ml | 4 fl oz |
| 1 cup | 237 ml | 8 fl oz |
| 1 pint | 473 ml | 16 fl oz |
| 1 quart | 946 ml | 32 fl oz |
Baking requires more precision than general cooking. Bread recipes need accurate water measurements for proper dough hydration. Cake batters require precise liquid ratios for correct texture. A 5% measurement error in liquids can affect rising, browning, and final product texture.
Beverage Serving Sizes
Standard beverage containers use different volume measurements by region. US beverage manufacturers label products in fluid ounces. International brands use milliliters. A standard beverage can contains 355 milliliters (12 US fluid ounces). Single-serve bottles typically hold 500 milliliters (16.9 US fluid ounces).
| Container Type | Milliliters | US Fluid Ounces |
|---|---|---|
| Small cup (coffee shop) | 240 ml | 8 fl oz |
| Standard can | 355 ml | 12 fl oz |
| Medium cup (coffee shop) | 355 ml | 12 fl oz |
| Single-serve bottle | 500 ml | 16.9 fl oz |
| Large cup (coffee shop) | 590 ml | 20 fl oz |
| Sports bottle | 750 ml | 25.4 fl oz |
| 1 liter bottle | 1000 ml | 33.8 fl oz |
Coffee shops use their own sizing conventions. A “tall” typically measures 355 milliliters (12 ounces), “grande” holds 473 milliliters (16 ounces), and “venti” contains 591 milliliters (20 ounces) for cold beverages. These measurements remain consistent across franchise locations for standardized recipes and portion control.
Daily Hydration Guidelines in ml & oz
Health organizations recommend daily water intake based on body weight, activity level, and climate. General guidelines suggest 2000-3000 milliliters (67-101 US fluid ounces) daily for adults. Athletes and people in hot climates require additional hydration.
Recommended Daily Water Intake
| Category | Milliliters per Day | US Fluid Ounces per Day |
|---|---|---|
| Women (sedentary) | 2200 ml | 74 fl oz |
| Men (sedentary) | 3000 ml | 101 fl oz |
| Active adults (moderate exercise) | 3500-4000 ml | 118-135 fl oz |
| Athletes (intense training) | 4000-6000 ml | 135-203 fl oz |
| Hot climate / outdoor work | 4500-5500 ml | 152-186 fl oz |
Individual hydration needs vary based on sweat rate, metabolic rate, and environmental conditions. Dehydration symptoms include dark urine, fatigue, and reduced physical performance. Proper hydration supports kidney function, temperature regulation, and nutrient transport throughout the body.
Baby Feeding Measurements
Formula preparation instructions specify exact milliliter amounts per feeding. Baby bottles display both milliliter and fluid ounce markings for accurate measurement regardless of recipe source.
Newborns typically consume 60-90 milliliters (2-3 US fluid ounces) per feeding during the first few weeks. By three months, feeding volumes increase to 120-180 milliliters (4-6 US fluid ounces) per feeding. Six-month-old infants consume 180-240 milliliters (6-8 US fluid ounces) per feeding. These measurements apply to both formula and expressed breast milk.
Typical Baby Feeding Volumes by Age
| Age | Milliliters per Feeding | US Fluid Ounces per Feeding | Feedings per Day |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0-2 weeks | 60-90 ml | 2-3 fl oz | 8-12 |
| 2-4 weeks | 90-120 ml | 3-4 fl oz | 6-8 |
| 1-3 months | 120-150 ml | 4-5 fl oz | 5-6 |
| 3-6 months | 180-210 ml | 6-7 fl oz | 4-5 |
| 6-12 months | 210-240 ml | 7-8 fl oz | 3-4 |
Formula preparation requires following manufacturer instructions exactly. Concentrated liquid formula requires dilution with specific water volumes. Powder formula needs precise water-to-powder ratios. Incorrect dilution can cause digestive problems or inadequate nutrition.
Medical Dosing and Liquid Medications
Liquid medication dosing requires precise milliliter measurements. Pharmacy instructions specify doses in milliliters. Some packaging includes both milliliter and fluid ounce markings on measuring devices. Medical professionals worldwide use metric measurements exclusively for prescription accuracy.
Common medication droppers and syringes measure in 0.1 milliliter increments. Typical pediatric doses range from 2.5 to 10 milliliters depending on medication concentration and child weight. Adult liquid medications typically use 5, 10, or 15 milliliter doses measured with provided dosing cups.
Never convert medication doses without consulting healthcare providers. Pharmacists calculate appropriate volumes based on prescription specifications. Using incorrect measuring devices or rounding conversions can result in under-dosing or over-dosing.
Product Labeling Standards
Consumer product regulations require volume labeling in both metric and imperial units in many countries. United States nutrition labels list serving sizes in milliliters alongside fluid ounces. European products entering US markets must display both measurement systems for regulatory compliance.
Cosmetic and personal care products show volumes in milliliters globally. Manufacturers export products internationally using metric labeling as the primary standard. US market versions add fluid ounce equivalents for consumer familiarity. Shampoo bottles, lotions, and skincare products typically range from 30 milliliters (1 fluid ounce) travel sizes to 750 milliliters (25.4 fluid ounces) for large containers.
Common Product Container Sizes
| Product Type | Standard Size (ml) | US Fluid Ounces |
|---|---|---|
| Travel/sample size | 30 ml | 1 fl oz |
| Small bottle (serum, oil) | 50 ml | 1.7 fl oz |
| TSA-approved travel size | 100 ml | 3.4 fl oz |
| Medium bottle (lotion, cream) | 250 ml | 8.5 fl oz |
| Standard shampoo bottle | 375 ml | 12.7 fl oz |
| Large bottle (body wash, shampoo) | 500 ml | 16.9 fl oz |
| Economy/family size | 750 ml | 25.4 fl oz |
Air travel restrictions limit liquid containers to 100 milliliters (3.4 US fluid ounces) in carry-on luggage. Manufacturers specifically produce travel-size products meeting this requirement. Larger containers require checked baggage or purchase after security screening.
Measurement Precision For ml to oz
Different applications require different precision levels. Home cooking typically uses measurements accurate to 5-10 milliliters. Baking benefits from 1-2 milliliter precision. Laboratory work requires 0.01-0.1 milliliter accuracy using calibrated pipettes and burettes.
Precision by Application
| Application | Required Precision | Measuring Device |
|---|---|---|
| General cooking | ±5-10 ml | Measuring cups, spoons |
| Baking | ±1-2 ml | Graduated measuring cups |
| Baby formula | ±2-3 ml | Marked baby bottles |
| Liquid medication | ±0.5 ml | Oral syringe, dropper |
| Scientific experiments | ±0.01-0.1 ml | Pipettes, burettes |
| Analytical chemistry | ±0.001 ml | Micropipettes |
Kitchen measuring cups vary in accuracy. Molded plastic measuring cups typically have ±5-10 milliliter tolerances. Glass graduated cylinders provide ±1-2 milliliter accuracy. Digital kitchen scales measuring liquids achieve ±1 gram precision, equivalent to ±1 milliliter for water-based liquids.
Temperature affects liquid volume measurements. Water expands approximately 0.02% per degree Celsius. Room temperature variations of 10-15°C create 0.2-0.3% volume differences. For most cooking applications, this remains negligible. Laboratory work requires temperature-controlled measurements for accurate results.
International Recipe Adaptation
Converting recipes between measurement systems requires attention to ingredient density differences. Liquid ingredients convert directly between milliliters and fluid ounces using standard factors. Some recipes list ingredients by weight rather than volume, requiring separate conversion considerations.
British recipes using imperial measurements differ from both US customary and metric systems. A UK pint equals 568 milliliters compared to 473 milliliters for a US pint. UK tablespoons measure 17.7 milliliters while US tablespoons equal 14.8 milliliters. These differences affect recipe outcomes when substituting measurement systems without proper conversion.
Australian recipes typically use metric measurements exclusively. Canadian recipes may use either metric or imperial depending on publication date and target audience. Modern international cookbooks provide measurements in multiple systems for wider accessibility. Digital recipe platforms increasingly default to metric measurements with optional unit switching.